1.原码
十进制数据的二进制表现形式,最左边的是符号位,0为正,1为负
利用原码对正数进行计算,正常相加
如果是负数计算,则需要利用反码
只有正数计算,使用原码进行计算
2.反码
为了解决原码不能计算负数的问题
计算规则:
正数的反码不变
负数的反码在原码的基础上,符号不变。数值取反,0变1,1变0如果负数计算,没有跨0,没有问题
如果负数计算,跨0,则需要利用补码
只有负数计算,使用反码进行计算
3.补码
为了解决负数计算时,跨0的问题
补码计算规则
正数的补码不变
负数的补码在反码的基础上+1
补码多记录一个特殊的值 -128 ,该数据在1个字节下,没有原码和反码若存在跨0的计算,使用补码进行计算
注意:计算机中的存储和计算都是以补码的形式进行
4.应用
基本数据类型
隐式转换(小变大) 前面补0
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 10; // 0000 1010
int b = a; // 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010
System.out.println(b);
}
}强制转换 去掉前面多的字节
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 300; // 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0010 1100
byte b = (byte)a; // 0010 1100 (去掉前面多的字节)
System.out.println(b); //44
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 200; // 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1100 1000
byte b = (byte)a; // 1100 1000 (去掉前面多的字节)
System.out.println(b); // -56
}
}
其他运算符
// & 逻辑与
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 200;
byte b = 10;
System.out.println(a & b); //两个都为1(true),则结果才为1
}
}
// | 逻辑或
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 200;
byte b = 10;
System.out.println(a | b); //只要有一个为1(true),则结果为1
}
}
// << 左移
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 200;
System.out.println(a << 2); // 左移两次
}
}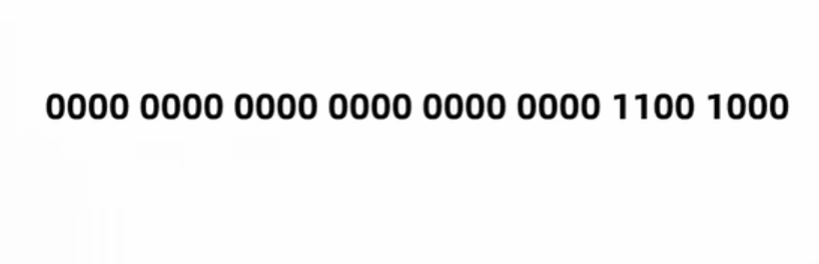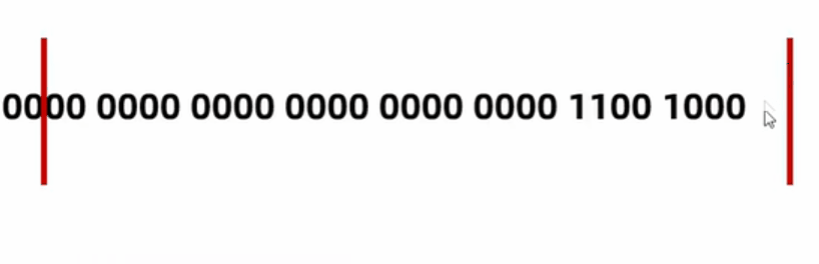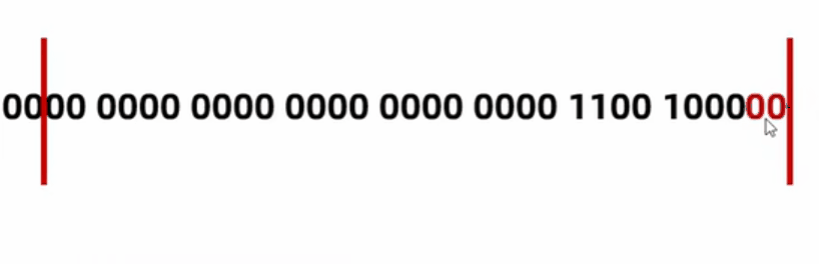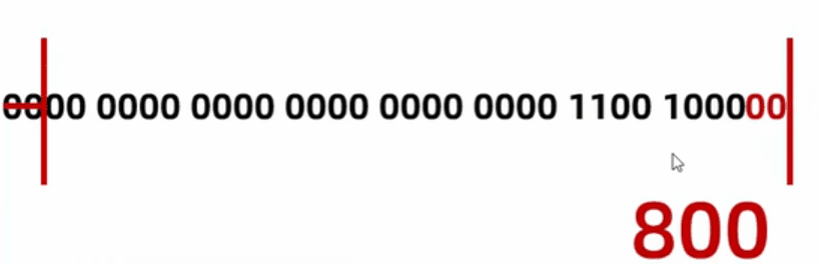
// >> 右移
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 200;
System.out.println(a >> 2); // 右移两次
}
}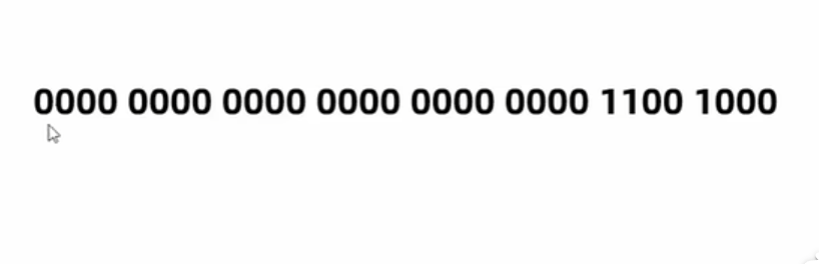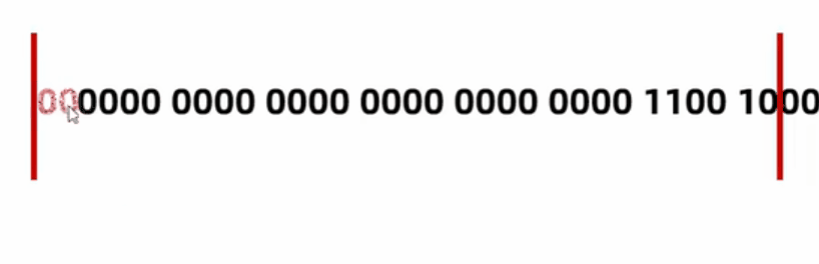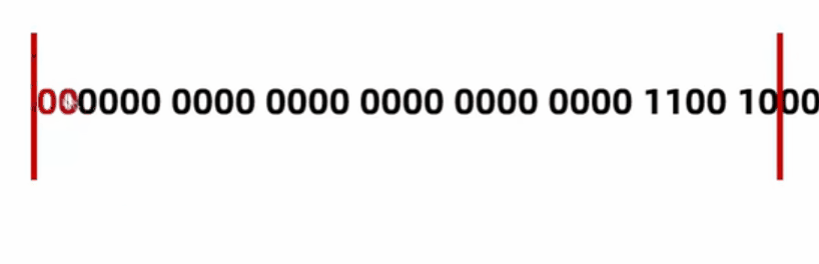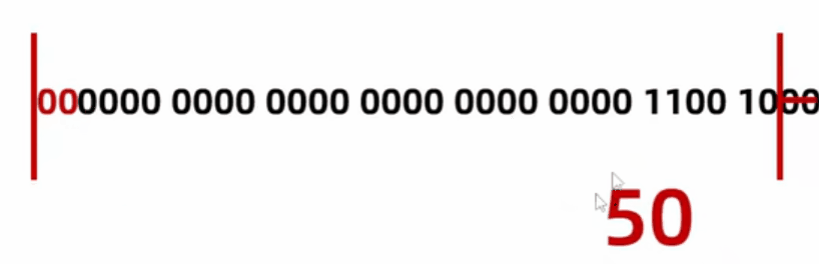


评论区