11 Nginx
1、概述
原名:engine x
F5:做硬件负载均衡(收购了Nginx,软件负载均衡)
Nginx优势:内存利用率高,并发能力高
工作模式:
master-worker(类似于apache的worker(多进程、多线程))
特点:
1)稳定性高(始终有预留进程)
2)配合Linux(cpu亲和,利用cpu优势,提升性能)
3)支持软重启(平滑升级、reload)
单用户模式:(只有一个进程)
进行工具测试,不支持nginx的平滑升级
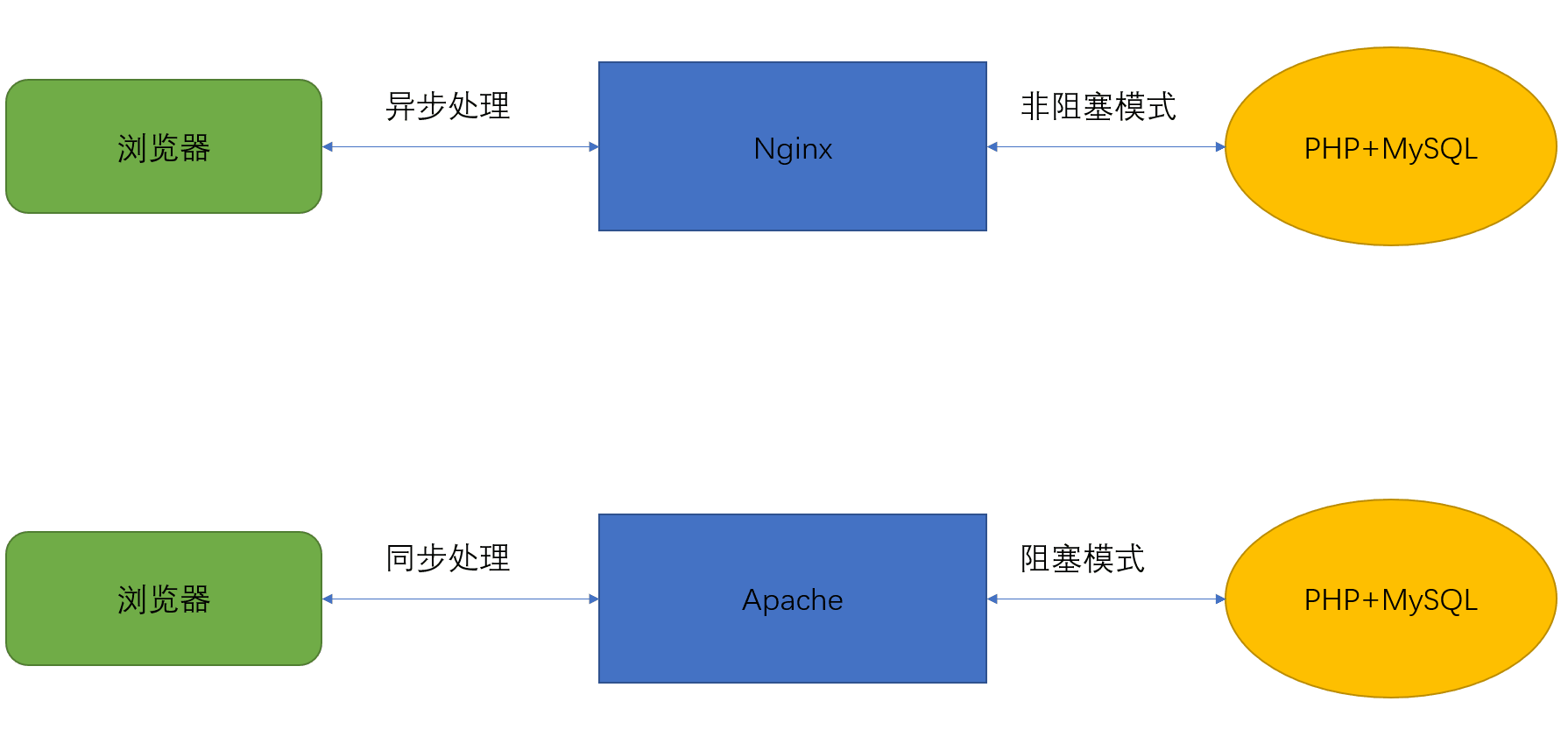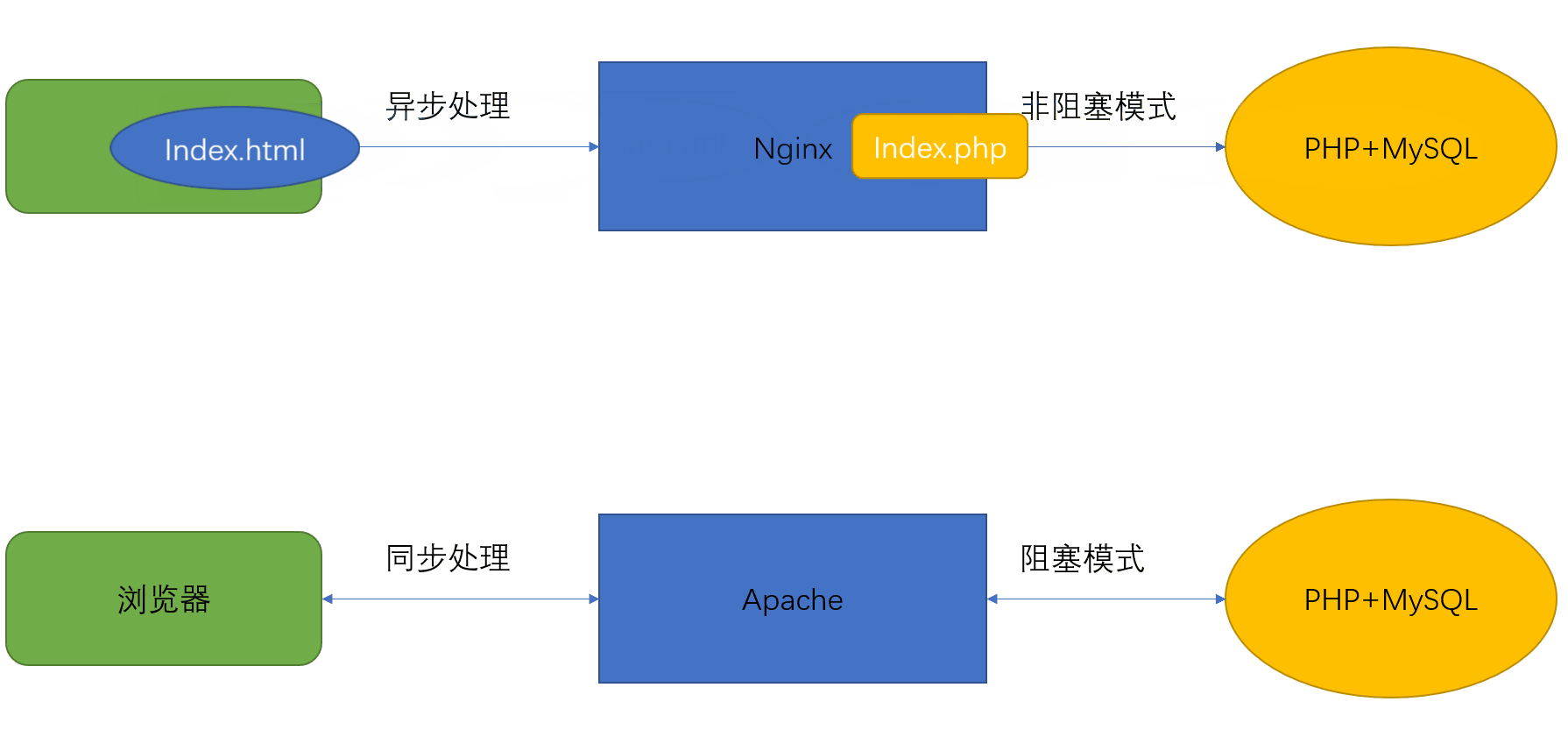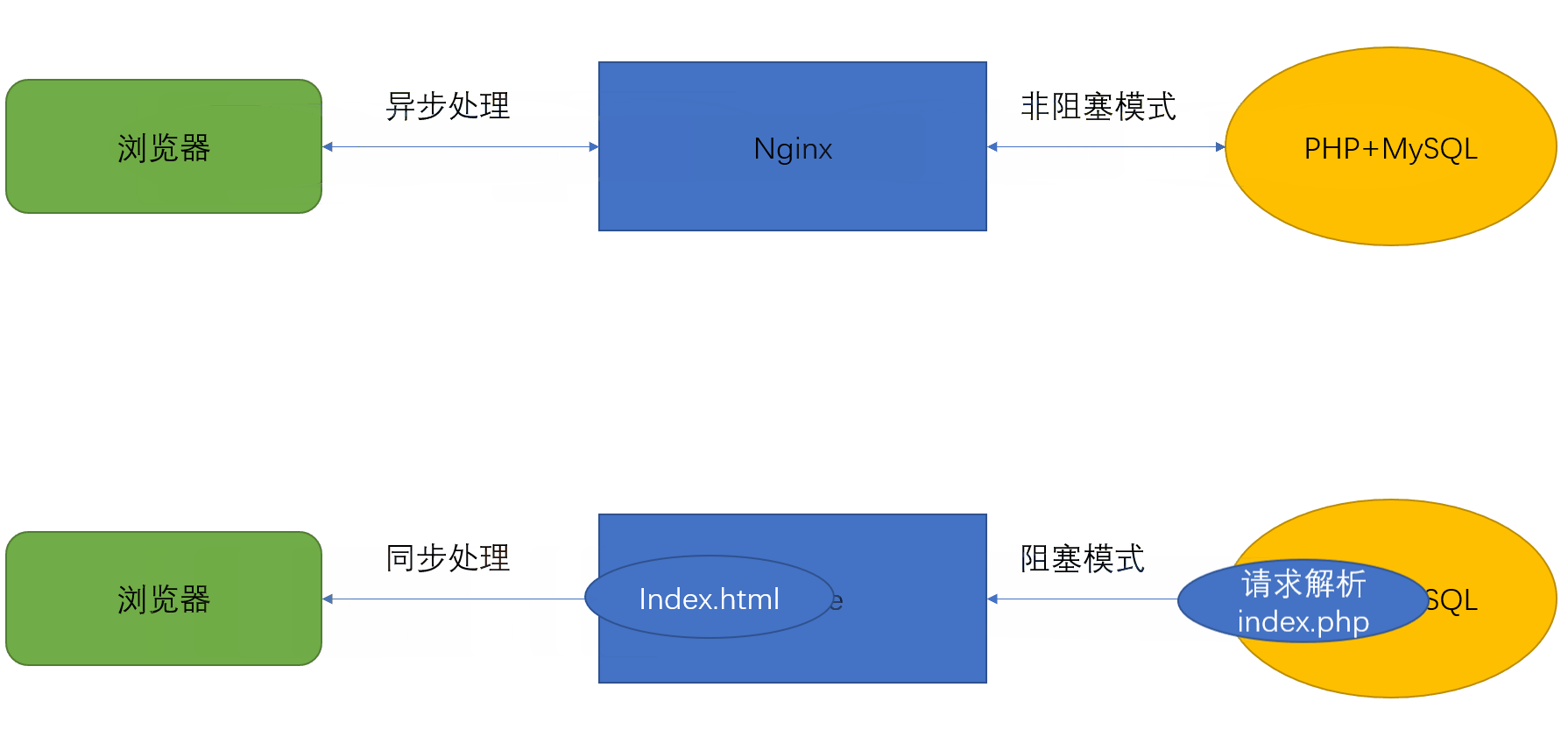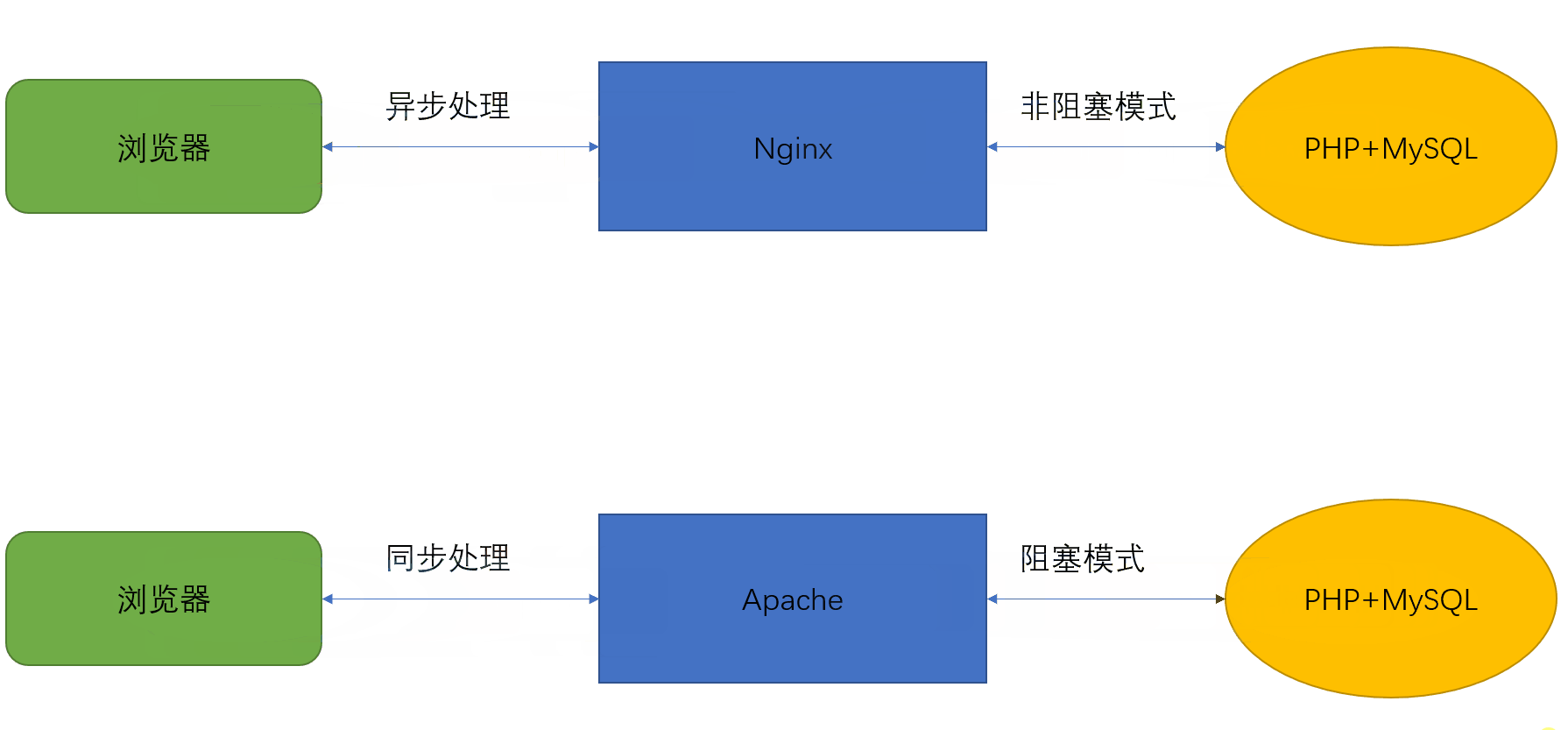
LAMP工作原理:
静态 ——》 server直接回传页面给client
动态 ——》 server ——》PHP ——》 回传解析后的页面给client
判断动静态:(看client是否访问数据库)
访问数据库:动态
不访问数据库:静态

LNMP工作原理:

LAMP、LNMP比较:
nginx在处理client请求时,作为server端
nginx在处理需要php请求时,作为php的client端
阻塞与非阻塞:
阻塞与非阻塞的重点在于进/线程等待消息时候的行为,也就是在等待消息的时候,当前进/线程是挂起状态,还是非挂起状态。
**阻塞:**调用在发出去后,在消息返回之前,当前进/线程会被挂起,直到有消息返回,当前进/线程才会被激活
**非阻塞:**调用在发出去后,不会阻塞当前进/线程,而会立即返回。
实例解释:
**阻塞取快递:**小明收到快递即将送达的信息后,什么事都不做,一直专门等快递。
**非阻塞取快递:**小明收到快递即将送达的信息后,等快递的时候,还一边敲代码、一边刷微信。
同步与异步,重点在于消息通知的方式;阻塞与非阻塞,重点在于等消息时候的行为。
所以,就有了下面4种组合方式
l 同步阻塞:小明收到信息后,啥都不干,等快递;
l 同步非阻塞:小明收到信息后,边刷微博,边等着取快递;
l 异步阻塞:小明收到信息后,啥都不干,一直等着快递员通知他取快递;
l 异步非阻塞:小明收到信息后,边刷着微博,边等快递员通知他取快递。
大部分程序的I/O模型都是同步阻塞的,单个进程每次只在一个文件描述符上执行I/O操作,每次I/O系统调用都会阻塞,直到完成数据传输。传统的服务器采用的就是同步阻塞的多进程模型。一个server采用一个进程负责一个request的方式,一个进程负责一个request,直到会话结束。进程数就是并发数,而操作系统支持的进程数是有限的,且进程数越多,调度的开销也越大,因此无法面对高并发。
Nginx采用了异步非阻塞的方式工作。我们先来先了解一下I/O多路复用中的epoll模型。
epoll****模型:
当连接有I/O事件产生的时候,epoll就会去告诉进程哪个连接有I/O事件产生,然后进程就去处理这个事件。
例如:小明家楼下有一个收发室,每次有快递到了,门卫就先代收并做了标记;然后通知小明去取送给小明的快递。
写个脚本:
探测主服务器是否故障,故障后切换从服务器
要求:1.故障检测
2.故障转移
前提:每个nginx服务器有两张网卡(ens33为管理,ens36为nginx访问(ip为203))
/root/nginx.txt中写入 nginx作为被访问的ip
/root/server.txt中写入被管理的ip
#!/bin/bash
cat << EOF
请检查以下配置是否完成:
1.nginx.txt(访问nginx的ip)
2.server.txt(管理nginx的多个服务器ip)
3.ssh能免密登录nginx服务器
4.nginx服务器都有两张网卡,且ens33为nginx服务器管理ip(201|202),ens36为nginx访问ip(203)
EOF
read -p "是否完成上述配置,文件到/root/目录中(y/n)" aa1
[ $aa1 == y ] && echo "ok" || exit
yum -y install nmap > /dev/null
aa2=$(cat /root/nginx.txt)
aa3=$(cat /root/server.txt)
echo "正在检测 $aa2 的nginx服务状态"
while true
do
sleep 1
aa4=$(nmap -sT $aa2 |egrep "http|rpcbind|mysql" |egrep "80|111|3306" |wc -l)
if [ $aa4 == "3" ];then
echo "runing ok"
else
for i in $(cat /root/server.txt)
do
ssh 192.168.18.$i 'aa5=$(netstat -anpt |grep nginx);if [ -z "$aa5" ];then ifdown ens36 ; else ifup ens36 > /dev/null; fi'
done
fi
done
测试:201,202分别启停nginx,判断ens36网卡启用状态

2、实验
1)负载均衡
注意:nginx.conf 中不能同时存在两个正则表达式(会有冲突)
upstream 模块:负载均衡模块、虚拟服务器组模块
拓展补充:wrr算法实现加权轮询(后期集群再讲更多算法类型和功能)
upstream bbs {
server 192.168.88.100:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.88.200:80 weight=2;
7-1 LNMP
主配置文件中:
1.在server标签前加入:
upstream apache {
server 192.168.18.202:80;
server 192.168.18.203:80;
}
2.在server标签中的location中写入 proxy_pass
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
proxy_pass http://apache; #加入此行
}
注意:upstream模块写在server上面
proxy_pass写在server标签中,一般在location正则中 { proxy_pass }
7-2 LAMP(源码安装的)
写入index.html、index.php
7-3 LAMP(rpm安装的)
yum 安装 httpd、mariadb-server、mariadb、php
启动httpd、mariadb
写入index.html、index.php
测试:在客户端调用201的index.html、index.php,判断是否实现均衡负载

2)nignx状态统计
注意:配置文件结尾有 ;
改完配置文件后需要重新加载配置: nginx -s reload
pkill -HUP nginx
热插拔:开机状态下能断开、连接
主配置文件中选项:
keepalive_timeout :保持keepalive状态的最大时间(keepalive的存在,降低了客户端与服务端反复的TCP连接)
实验步骤:
1.在nginx主配置文件中,server标签中单独写一个 location 标签
(前提:在源码包安装nginx时,需要有 --with-http_stub_status_module)
location /tongji {
stub_status on; #启用状态统计
access_log off; #不记录日志
}
2.重新加载nginx配置、测试
测试:在客户端打开浏览器输入地址,进行nginx状态统计


3)目录保护
实现对状态统计界面的保护
(需要在location 标签中加入 auth_basic、auth_basic_user_file)
步骤:
1.在主配置文件中,状态统计标签的location 中加入
location /tongji {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
auth_basic "Welcome To YQ's Nginx tongji"; #在此处新增两行
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/htpasswd.nginx;
}
2.安装htpasswd命令(属于httpd-tools包),实现:创建、新增加密目录的登录用户
1) yum 安装httpd-tools
2) 创建用户
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/htpasswd.nginx yq
加载nginx配置测试:

4)基于IP身份验证(访问控制)
在软件层面实现类似防火墙的功能,接着上一个实现往下进行
步骤:
在location 中定义 allow、deny
location /tongji {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
auth_basic "Welcome To YQ's Nginx tongji";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/conf/htpasswd.nginx;
allow 192.168.18.202; #新增此处开始的两行(仅允许192.168.18.202访问)
deny 0.0.0.0/0;
}
测试:

5)nginx虚拟主机(基于域名、且加密访问)
步骤:
修改主配置文件:
1.server_name选项中新增域名
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.a.com www.b.com;
access_log logs/host.access.log main;
.....
2.location / 标签中新增跳转规则
....
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
proxy_pass http://apache;
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://www.yq.com$1 permanent;
}
....
3.开启ssl 的server 标签,并配置好 location 规则、整数指向位置、解析php规则
....
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.yq.com;
ssl_certificate server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key server.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ \.php(/.*)*$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
}
....
4.到 /usr/local/nginx/conf 目录中创建证书
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/
[root@localhost conf]# openssl genrsa -out server.key
[root@localhost conf]# openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
[root@localhost conf]# openssl x509 -req -days 365 -sha256 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
5.检查语法、重新加载配置,测试
[root@localhost conf]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost conf]# nginx -s reload
测试:
客户端hosts文件为:
192.168.18.201 www.a.com
192.168.18.201 www.b.com
192.168.18.202 www.yq.com

6)nginx实现HTTP2
步骤:
1.停止nginx服务
2.重新解压nginx压缩包,加上开启http2模块再编译安装
[root@localhost conf]# cd /lnmp/
[root@localhost lnmp]# rm -rf nginx-1.12.2
[root@localhost lnmp]# tar -xf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
[root@localhost lnmp]# cd nginx-1.12.2/
[root@localhost nginx-1.12.2]# ./configure --user=nginx --group=nginx --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module && make -j 8 && make install
3.在server标签中的 ”listen 端口“ 后加入http2
....
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
....
4.检查语法、启动nginx,测试
[root@localhost nginx-1.12.2]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@localhost nginx-1.12.2]# nginx -s reload
测试:
客户端hosts文件为:
192.168.18.201 www.a.com
192.168.18.201 www.b.com
192.168.18.202 www.yq.com

7)ab压力测试
属于httpd-tools(与统计模块相对应进行测试)
ab -n 10000 -c 1000 http://192.168.18.201/index.html
8)实现动态(.php)、静态(.jpg|jpeg|png|gif)分开代理
location \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.18.202;
}
location \.php$ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.18.203;
}